Uveitis - Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
07-04-2024
What is Uveitis?
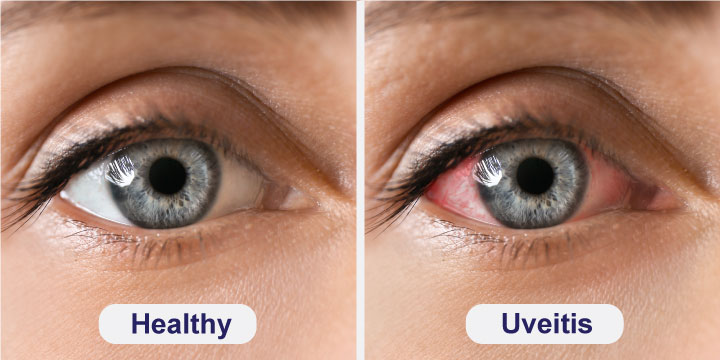
Uveitis is a condition that affects the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This inflammation of the uvea can cause redness, pain, and blurred vision. It is important for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek prompt medical attention from an eye care professional to prevent potential complications and preserve their vision.What Are The Causes Of Uveitis?
Uveitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammatory diseases, or underlying medical conditions. Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites can lead to uveitis, as can certain autoimmune diseases that cause the body's immune system to mistakenly attack the eye. Additionally, underlying medical conditions such as sarcoidosis, ankylosing spondylitis, or inflammatory bowel disease can also trigger uveitis. In some cases, the exact cause of uveitis may not be identified, making it a challenging condition to treat.What Are The Risk Factors For Uveitis?
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing uveitis. These include having certain underlying medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease, infections such as herpes simplex or tuberculosis, or a history of eye injury or surgery. Additionally, individuals who smoke or have a family history of uveitis may also be at higher risk for developing the condition. It is important for patients with these risk factors to be vigilant about their eye health and seek prompt medical attention if they experience any symptoms of uveitis.What Are The Symptoms Of Uveitis?
Symptoms of Uveitis may include eye redness, pain, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, and a feeling of floaters or spots in the field of vision. Some patients may also experience decreased vision, headaches, or a feeling of pressure in the eye. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as Uveitis can potentially lead to serious complications if left untreated.How is Uveitis Diagnosed?
Uveitis is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination conducted by an optometrist or ophthalmologist. During the examination, the eye doctor will closely inspect the eye for any signs of inflammation in the uvea, which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Specialized tests such as a slit lamp examination, tonometry, and dilated eye exam may also be performed to aid in the diagnosis of uveitis. Additionally, the doctor may ask about any symptoms the patient is experiencing and their medical history to help determine the underlying cause of the inflammation.How is Uveitis Treated?
Treatment for Uveitis typically involves addressing the underlying cause of inflammation, if known, and reducing eye discomfort and swelling. In many cases, corticosteroid eye drops are prescribed to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In more severe cases, oral corticosteroids or corticosteroid injections may be necessary. Additionally, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or immunosuppressive medications may be used to help control inflammation. In some cases, dilation of the pupil and wearing sunglasses to reduce light sensitivity may also be recommended. It is important for individuals with Uveitis to follow up regularly with their eye care provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.Is There A Cure For Uveitis?
While there is no specific cure for Uveitis, treatment options are available to help manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. These treatments typically include prescription eye drops, oral medications, or injections to reduce inflammation and pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to address complications or persistent inflammation. It is important for individuals with Uveitis to work closely with their eye care provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs and to monitor the condition closely to prevent further complications.How Can Uveitis Be Prevented?
Uveitis can be prevented by taking steps to maintain overall eye health and reduce the risk of inflammation in the eye. This includes regular eye exams to monitor for any potential issues, wearing protective eyewear in situations where the eyes may be exposed to injury or irritants, and practicing good hygiene to prevent infections that could lead to uveitis. Additionally, managing underlying health conditions that may increase the risk of developing uveitis, such as autoimmune diseases, can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing inflammation in the eye. By being proactive in caring for the eyes and overall health, individuals can help prevent uveitis from occurring.Regular eye exams with advanced technologies are essential for the early detection and treatment of uveitis. Schedule an eye exam with an optometrist today!
Schedule An Appointment
Adult Eye Exams
Our advanced eye exams consist of 25+ modern tests and digital scans to assess eye health, function, and visual acuity.

Child Eye Exams
Give your child a clear future with an annual eye exam from our experienced Edmonton optometrists.

Senior Eye Exams
Maintain your vision through your golden years with gold standard eye care from the optometrists at our Edmonton eye clinic.

Contact Lens Eye Exams
Our eye exams for contact lens wearers include test and digital scans to assess eye health, function, visual acuity, and lens fit.
Diabetic Eye Exams
Managing diabetes requires regular eye exams to ensure that diabetes is not causing irreversible vision loss.

Dilated Eye Exams
Dilating the eyes enables our Edmonton optometrists to see more of the eye so that you many never see less.
Our Edmonton Eye Exams Are Comprised Of 4 Phases Of Evaluation
1. Eye Exam Pre-Testing
Corneal Thickness | Intraocular Pressures | Visual Field
Pre-testing is a detailed process that gathers all necessary information for the optometrist in advance of the optometrist-administered eye examination. This process involves completing a detailed patient history, as well as a series of standard tests. Pre-testing is an essential part of the comprehensive eye exam process, providing valuable information and visuals for both the optometrist and the patient.
More About Pre-Testing »
2. Advanced Diagnostic Testing
Retinal Photography, OCT, Topography
eye-deology Vision Care differentiates itself from other clinics by having the most advanced modern diagnostic specialty testing equipment. Specialty equipment, such as a wide-angle high-resolution retinal imager, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), Humphrey Visual Field Analyzer and corneal topographer, ensures that patients receive the best comprehensive eye care.
More About Advanced Testing »
3. Optometrist Examination
Health Assessment & Disease Diagnosis
eye-deology Vision Care Edmonton optometrists perform a multitude of tests and assessments to evaluate ocular health, eye coordination, and visual acuity. In addition, they also evaluate the results of the tests and scans performed during pre-testing. As part of patient education, our optometrists also take the time to show and explain results to patients.
More About Doctor Exam »
4. Eye Glass Consult
Prescription | Lens Selection | Digital Fitting
If you require corrective lenses to improve your vision, our licensed opticians will customize their fit to your unique attributes, needs, lifestyle, and budget. Our opticians are happy to provide you with information about the latest eyeglass frame and lens technologies available so you can make informed decisions and begin seeing and looking your best.
More About Eyewear Consult »