Corneal Ulcers
11-07-2016
Symptoms of a corneal ulcer include a painful red eye with mild to severe eye discharge and reduced vision. The condition results from a localized infection of the cornea. In most cases, corneal ulcers are due to a bacterial infection of the cornea — often following damage or trauma to the eye.
Individuals that wear contact lenses are particularly susceptible to eye irritation that can lead to corneal ulcers. A contact lens may rub against the eye's surface, creating slight damage to the epithelium that may allow bacteria to penetrate the eye. Contact lens wearers can avoid corneal ulcers by practising good hygiene, such as washing their hands before handling lenses. In addition to bacterial infection, corneal ulcers can also be caused by fungi, parasites and/or the herpes simplex virus (ocular herpes). Other conditions that lead to the development of corneal ulcers include severely dry eyes, eye allergies and/or general infections. Immune system disorders and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis and psoriasis also commonly lead to the development of corneal ulcers.
If an optometrist suspects that bacteria are the cause of the corneal ulcer in question, they will typically prescribe topical antibiotics. Most optometrists will see patients with corneal ulcers every one to three days, depending on the severity of the condition. Recovery times vary and depend largely on the location of the ulcer. If the ulceration is located in the central cornea, the condition usually takes longer to go away, and vision may be reduced permanently due to scarring. Unfortunately, permanent damage and vision loss may occur, even if the condition is identified and treated early.
If you suspect that you may have a corneal ulcer, please see an optometrist immediately. In Edmonton, visit the optometrists at Eye-deology Vision Care.
Schedule An Appointment
Adult Eye Exams
Our advanced eye exams consist of 25+ modern tests and digital scans to assess eye health, function, and visual acuity.
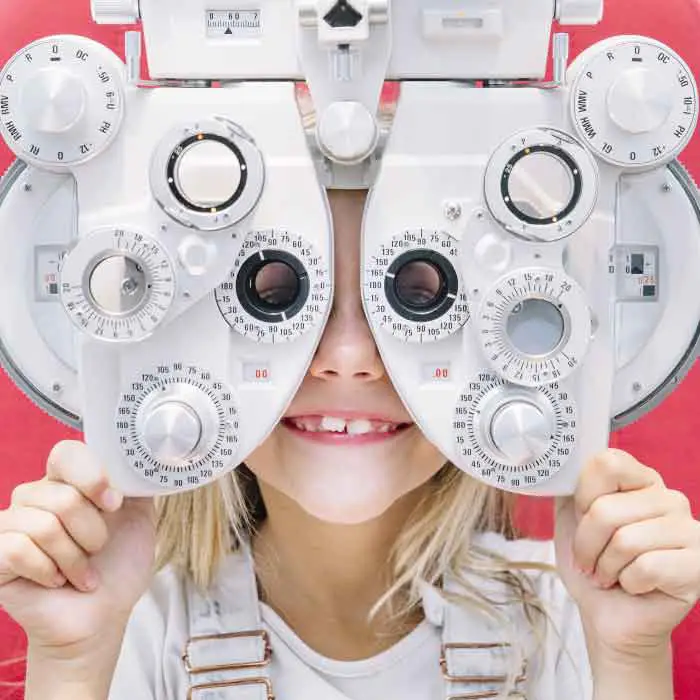

Child Eye Exams
Give your child a clear future with an annual eye exam from our experienced Edmonton optometrists.
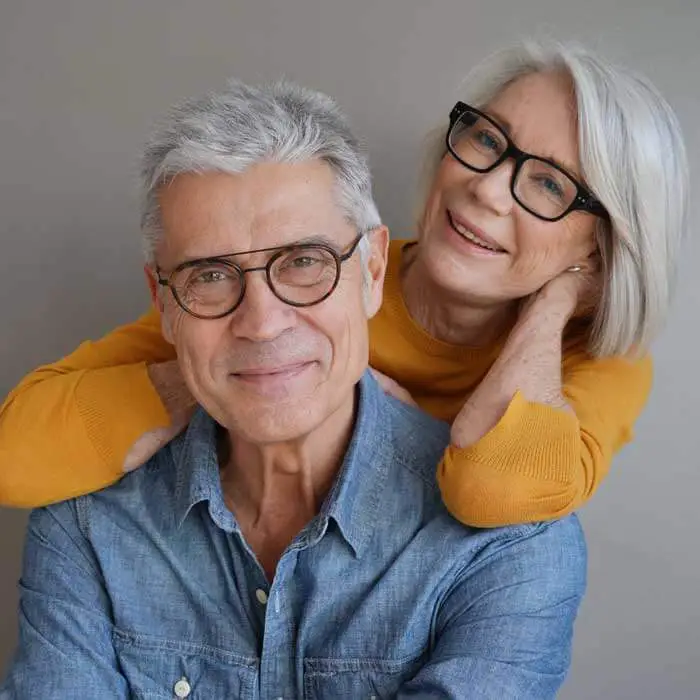

Senior Eye Exams
Maintain your vision through your golden years with gold standard eye care from the optometrists at our Edmonton eye clinic.
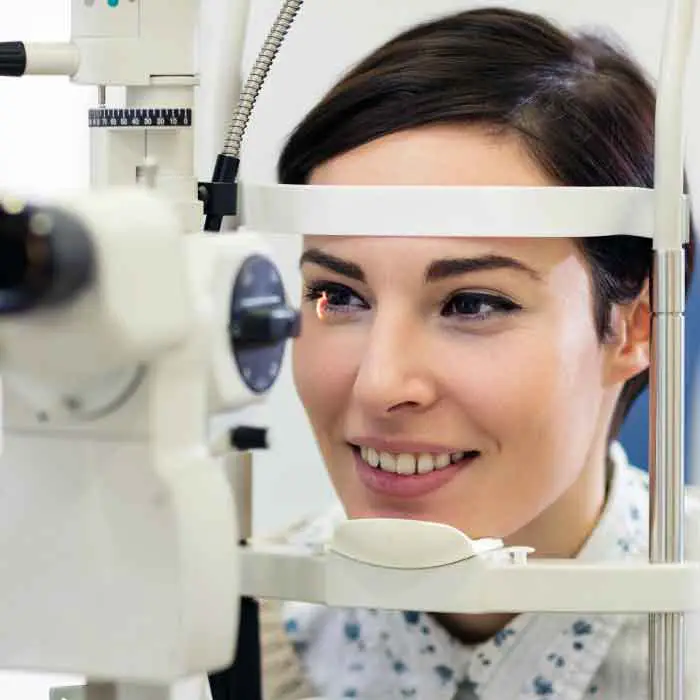

Contact Lens Eye Exams
Our eye exams for contact lens wearers include test and digital scans to assess eye health, function, visual acuity, and lens fit.
Diabetic Eye Exams
Managing diabetes requires regular eye exams to ensure that diabetes is not causing irreversible vision loss.
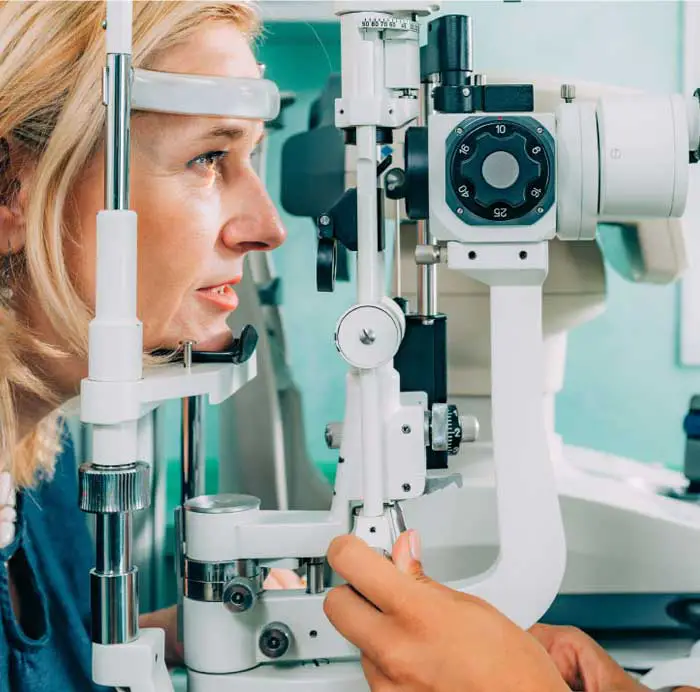

Dilated Eye Exams
Dilating the eyes enables our Edmonton optometrists to see more of the eye so that you many never see less.
Our Edmonton Eye Exams Are Comprised Of 4 Phases Of Evaluation
1. Eye Exam Pre-Testing
Corneal Thickness | Intraocular Pressures | Visual Field
Pre-testing is a detailed process that gathers all necessary information for the optometrist in advance of the optometrist-administered eye examination. This process involves completing a detailed patient history, as well as a series of standard tests. Pre-testing is an essential part of the comprehensive eye exam process, providing valuable information and visuals for both the optometrist and the patient.
More About Pre-Testing »
2. Advanced Diagnostic Testing
Retinal Photography, OCT, Topography
eye-deology Vision Care differentiates itself from other clinics by having the most advanced modern diagnostic specialty testing equipment. Specialty equipment, such as a wide-angle high-resolution retinal imager, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), Humphrey Visual Field Analyzer and corneal topographer, ensures that patients receive the best comprehensive eye care.
More About Advanced Testing »
3. Optometrist Examination
Health Assessment & Disease Diagnosis
eye-deology Vision Care Edmonton optometrists perform a multitude of tests and assessments to evaluate ocular health, eye coordination, and visual acuity. In addition, they also evaluate the results of the tests and scans performed during pre-testing. As part of patient education, our optometrists also take the time to show and explain results to patients.
More About Doctor Exam »
4. Eye Glass Consult
Prescription | Lens Selection | Digital Fitting
If you require corrective lenses to improve your vision, our licensed opticians will customize their fit to your unique attributes, needs, lifestyle, and budget. Our opticians are happy to provide you with information about the latest eyeglass frame and lens technologies available so you can make informed decisions and begin seeing and looking your best.
More About Eyewear Consult »